What is a content management system (CMS) ?
Ok, so a content management system (CMS) manages the creation and modification of your digital content.
It typically allows access to multiple users to be able to edit your sites content in a collaborative environment.
CMS features vary enormously. Most CMSs will include some Web-based publishing, format management, possibly a historical record or log of editing and even version control, indexing, search, and retrieval.
A web content management system (WCMS) is a CMS designed to support the management of the content of Web pages. Most popular CMSs are also WCMSs. Web content includes text and embedded graphics, photos, video, audio, maps, and programme or source code (e.g., for applications) that displays content or interacts with the end user.
Such a content management system (CMS) typically has two major components:
- A content management application (CMA) is the front-end user interface that allows a user, even with limited expertise, to add, modify, and remove content from a website without the intervention of an experienced user, designer, developer or webmaster.
- A content delivery application (CDA) compiles that information and updates the website.
Digital asset management systems are another type of CMS. They manage the content with clearly defined author or ownership, such as documents, movies, pictures, phone numbers, and so on. Conceivably, business could also utilise a CMS to store, control, revise, and publish it’s documentation.
Based on market share statistics, the most popular content management system is WordPress, used by approximately over 28% of all websites on the internet, and by around 2/3’s of all websites using a known content management system. Other popular content management systems include Joomla and Drupal
Common features
Content management systems typically provide the following features:
- SEO-friendly URLs
- Integrated and online help
- Modularity and extensibility
- User and group functionality
- Templating support for changing designs
- Install and upgrade wizards
- Integrated audit logs
- Compliance with various accessibility frameworks and standards.
- Reduced need to code from scratch
- Easy to create a unified look and feel
- Version control
- Edit permission management
Disadvantages
- Limited or no ability to create functionality not envisioned in the CMS (e.g., layouts, web apps, etc.)
- Increased need for special expertise and training for content authors
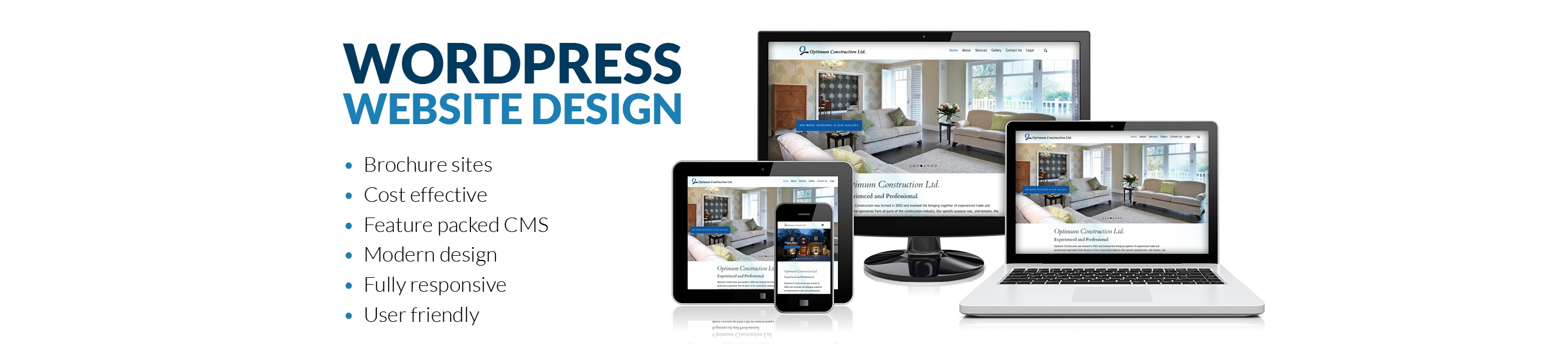
What CMS does WWD recommend and deploy?
- For the vast majority of our clients we would design, build and deploy your site using the WordPress CMS with the leading theme available, supported and maintained for life.
- For more complex needs beyond the scope of WordPress or for other technical reasons we would consider using our own bespoke, WWD-CMS.
- We would not consider building in Joomla or Drupal.